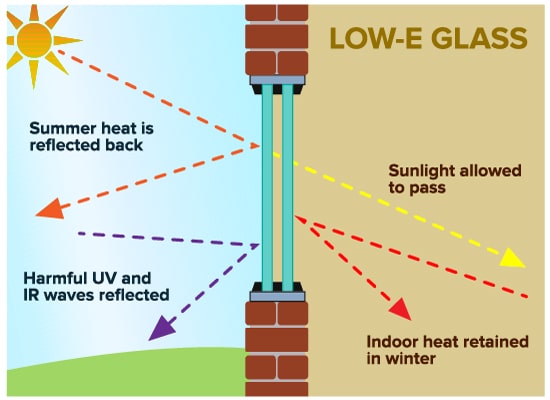
When upgrading or installing windows, choosing the right type of glass is crucial for improving energy efficiency and comfort. One of the most advanced options available today is Low-E glass, which offers a range of benefits and applications. Understanding the types of Low-E glass and their impact on your home can help you make informed decisions that save energy and enhance living spaces.
What Are Low-E Glass Coatings?
Low-E (low emissivity) glass coatings are specialized layers applied to glass surfaces to reduce heat transfer. These coatings are designed to reflect infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass through, resulting in enhanced insulation and energy efficiency. This makes Low-E glass a popular choice for modern windows.
Low-E glass coatings come in various types, each offering distinct benefits depending on the specific needs of your home. By reflecting heat, these coatings help maintain consistent indoor temperatures, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
Benefits of Low-E Window Glass
Low-E window glass incorporates these advanced coatings to provide several key advantages:
- Improved Insulation: Low-E glass helps to keep indoor temperatures stable by reducing heat loss in the winter and minimizing heat gain in the summer. This leads to greater comfort and lower energy bills.
- UV Protection: The coatings on Low-E glass block a significant portion of ultraviolet (UV) rays, which can cause fading of furniture, carpets, and artwork. This added protection helps preserve the interior of your home.
- Reduced Glare: Low-E coatings can reduce glare from sunlight, making it easier to view screens and enjoy natural light without discomfort.
- Enhanced Durability: Low-E glass is often treated with additional protective layers, increasing its resistance to environmental factors and extending its lifespan.
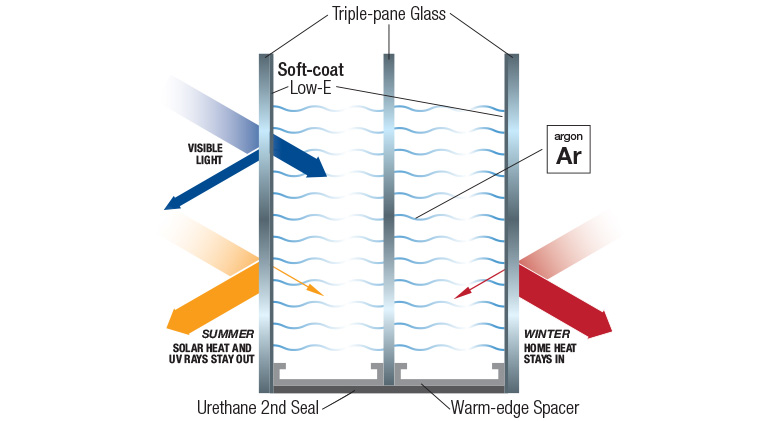
Types of Low-E Glass
There are several types of Low-E glass, each designed to address specific needs and performance criteria:
- Single Low-E Glass: This type features a single layer of Low-E coating, providing basic insulation and UV protection. It is a cost-effective option for homes with moderate energy efficiency needs.
- Double Low-E Glass: Incorporating two layers of Low-E coating, this type offers enhanced thermal performance and better insulation. It is ideal for homes in regions with extreme temperatures.
- Triple Low-E Glass: With three layers of Low-E coating, this glass provides superior insulation and energy efficiency. It is often used in high-performance buildings and areas with severe climate conditions.
| Type of Low-E Glass | Insulation Performance | UV Protection | Cost | Ideal Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Low-E | Moderate | Basic | Low | Homes with mild climates |
| Double Low-E | High | Enhanced | Moderate | Homes in extreme temperatures |
| Triple Low-E | Superior | Maximum | High | High-performance buildings |
Low-E Glass Applications
Low-E glass is versatile and can be used in various applications to enhance both residential and commercial properties:
- Windows and Doors: Low-E glass is commonly used in windows and doors to improve insulation and reduce energy consumption. It is available in different styles, including casement, sliding, and fixed windows.
- Skylights: For homes with skylights, Low-E glass can help reduce heat gain and loss while maintaining natural light.
- Curtain Walls: In commercial buildings, Low-E glass is often used in curtain walls to enhance energy efficiency and reduce glare.
Low-E Glass Technologies and Features
Advancements in Low-E glass technologies have led to a range of features designed to improve performance and aesthetics:
- Low-E Glass Performance: Modern Low-E glass technologies offer exceptional performance in terms of thermal insulation, UV protection, and glare reduction. The coatings are engineered to provide optimal efficiency across various climate conditions.
- Low-E Glass Features: Some Low-E glass products come with additional features such as self-cleaning coatings or enhanced durability. These features further contribute to the convenience and long-term value of Low-E glass.
Insulated Glass Units
Low-E glass is often used in insulated glass units (IGUs), which consist of two or more panes of glass separated by a spacer and filled with an insulating gas. IGUs enhance the overall energy efficiency of windows by providing additional layers of insulation and reducing heat transfer.
Conclusion
Incorporating types of Low-E glass into your windows is an effective way to enhance energy efficiency, comfort, and durability. By understanding the various types of Low-E glass and their applications, you can make informed choices that benefit your home and reduce energy consumption. Whether you’re building new or renovating, Low-E glass offers a range of benefits that contribute to a more sustainable and comfortable living environment.